Every home has something smart in it these days. Home Depot is selling a wider range of smart products every year, all of which can be purchased for less with a Home Depot Money Off Coupon from We Are Coupons. In amongst all the tech sits something we all take for granted today; Bluetooth. But have you ever wondered where is comes from?
The Wikipedia Definition of Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances (using short-wavelength UHF radio waves in the ISM band from 2.4 to 2.485 GHz) from fixed and mobile devices, and building personal area networks (PANs).
Bluetooth was developed by Ericcson, a Danish company and named it after a Danish king, whose nickname was Bluetooth because he brought the Danish tribes together.
This is not entirely true as Bluetooth was developed by Ericsson (pre-Sony Ericsson) which is a major Swedish telecommunication company. It was named after the Danish Viking king, Harald Blåtand who converted from the belief in the Ancient Norse Gods and Goddesses to the single God of Christianity. Blåtand translated to English, literally means Bluetooth.
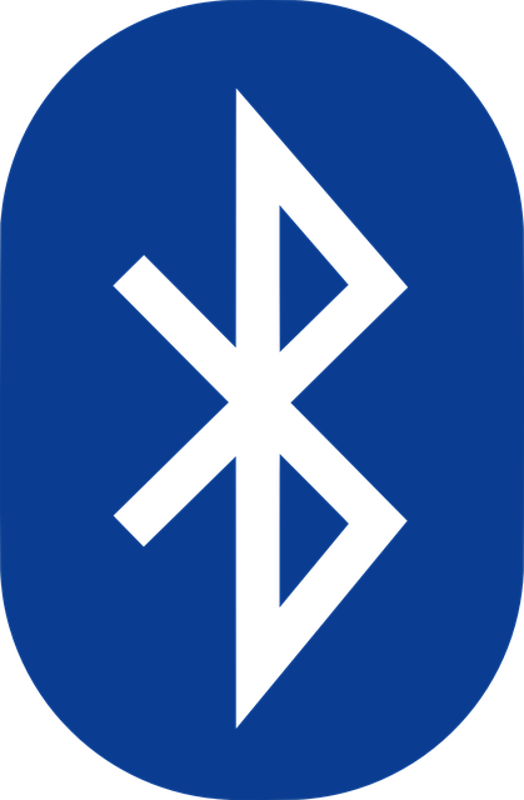
The Bluetooth symbol has Runic inscription in it. The two lines sticking out of the back of the B actually represent a Runic H and the B is Runic B. Harald Blåtand's initials form the symbol of today's world's Bluetooth!
Bluetooth Development
Bluetooth is supervised by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), which includes more than 25,000 member companies in the sectors of telecommunication, computing, network, and gadgets. The IEEE standardized Bluetooth as IEEE 802.15.1. The Bluetooth SIG oversees development of the specification, manages the qualification program, and protects the trademarks. Any company must meet Bluetooth SIG benchmarks to promote any product as a Bluetooth device. A network of patents connect with the technology to ensure certification of specific qualifying devices that meets the exceptional standards set down.
Bluetooth Specifications Today
The Bluetooth Core Specification Working Group (CSWG) has Four levels of specification:
The Bluetooth Core Specification - The release cycle is typically a few years
Core Specification Addendum (CSA) – The release cycle can be a few times per year
Core Specification Supplements (CSS) – Here the release cycle is very quick
Bluetooth and WiFi
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are somewhat complementary in their applications and use. Wi-Fi is access point-centered usually, with an asymmetrical client-server reference to all traffic routed through the access point, while Bluetooth is symmetrical usually, between two Bluetooth devices. Bluetooth acts well in simple applications where two devices need to hook up with minimal construction just like a button press, as with headsets and remote control controls, while Wi-Fi suits better in applications where some extent of customer construction is high and possible rates of speed will be required, specifically for network gain access to via and gain access to node. However, Bluetooth access points do exist and ad-hoc connections are possible with Wi-Fi though much less simply much like Bluetooth. Wi-Fi Direct was just lately developed to include a far more Bluetooth-like ad-hoc features to Wi-Fi.